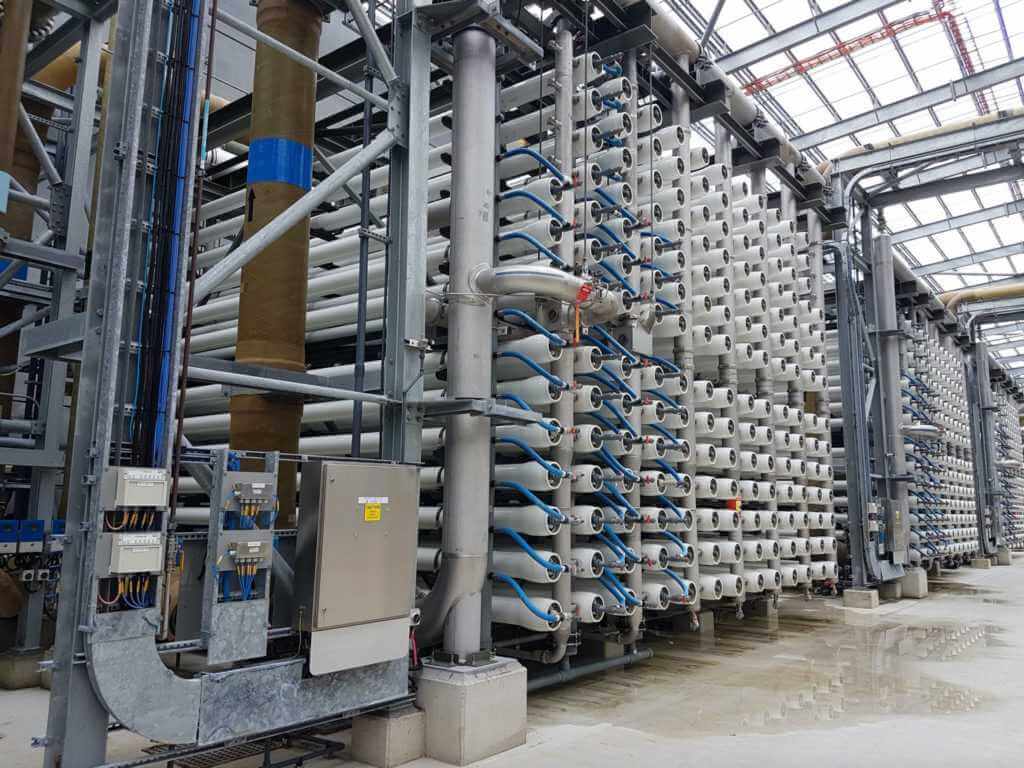
Reverse Osmosis in desalination is a process that forces salt water directly onto membranes at high pressure. These membranes are semi-permeable, biological or synthetic polymeric membranes that allow certain molecules or ions to pass through.
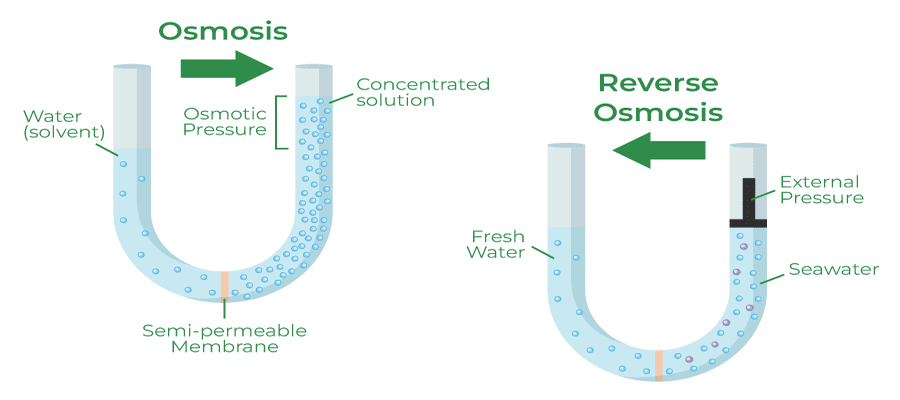
Osmosis is the movement of high-concentration water molecules through a membrane to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules. In other words, osmosis is the watering down of another solution. In the most simple terms, adding water to a cordial syrup is an example of osmosis.
Reverse Osmosis is the movement of low-concentration water molecules through a membrane to a solution that will have a higher concentration of water molecules.
Reverse Osmosis (RO), therefore, is the water treatment process by which contaminants (or, for example, salt) are removed. The result is a solution that has a higher concentration of water molecules because most other non-water particles have been stopped by the membrane.
Metal Maintenance has the capability to service the membranes used in reverse osmosis at desalination plants.
Find out more about this process from a recent project of ours.
